
Best Practices on Setting up Hyper-V Cluster Networks in Windows Server 2016
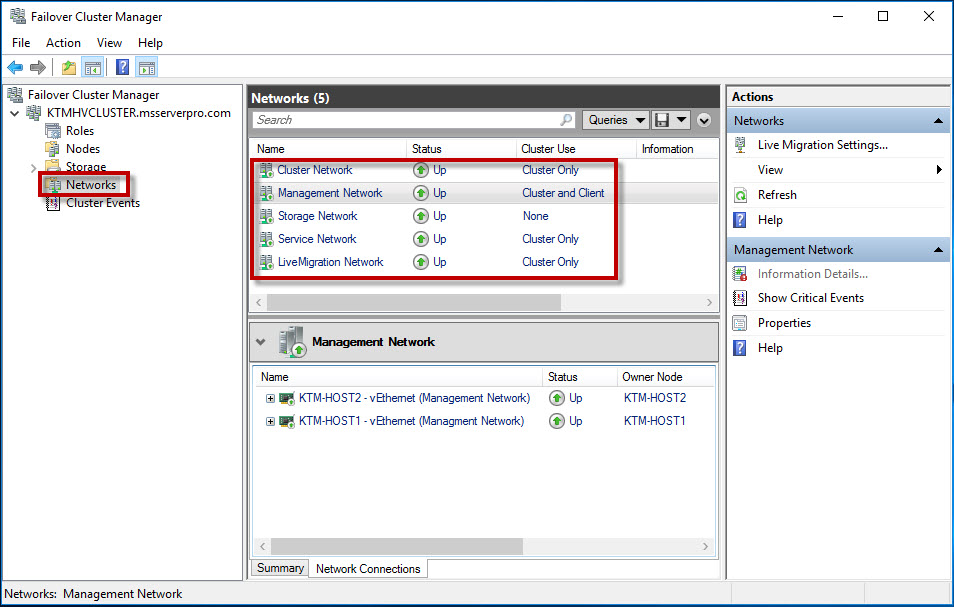
There is no single best recommendation on how many networks a Hyper-V host should have, and different factors such as storage type, Hyper-V features used and virtualization load. Networks and network adapters are important parts of each Hyper-V Cluster implementation. You cannot configure a cluster without configuring the networks that the cluster will use. A Hyper-V Cluster needs multiple types of communication between production networks, Hyper-V Hosts and storage system. When you deploy a Hyper-V cluster, you must plan for multiple types of network traffic. After you have completed a Hyper-V Cluster, cluster creates networks name as Cluster Network1, Cluster Network2, and Cluster Network3 and so on… You have to rename cluster network name as based on network traffic type as given below. Then configure network type recommended setting.
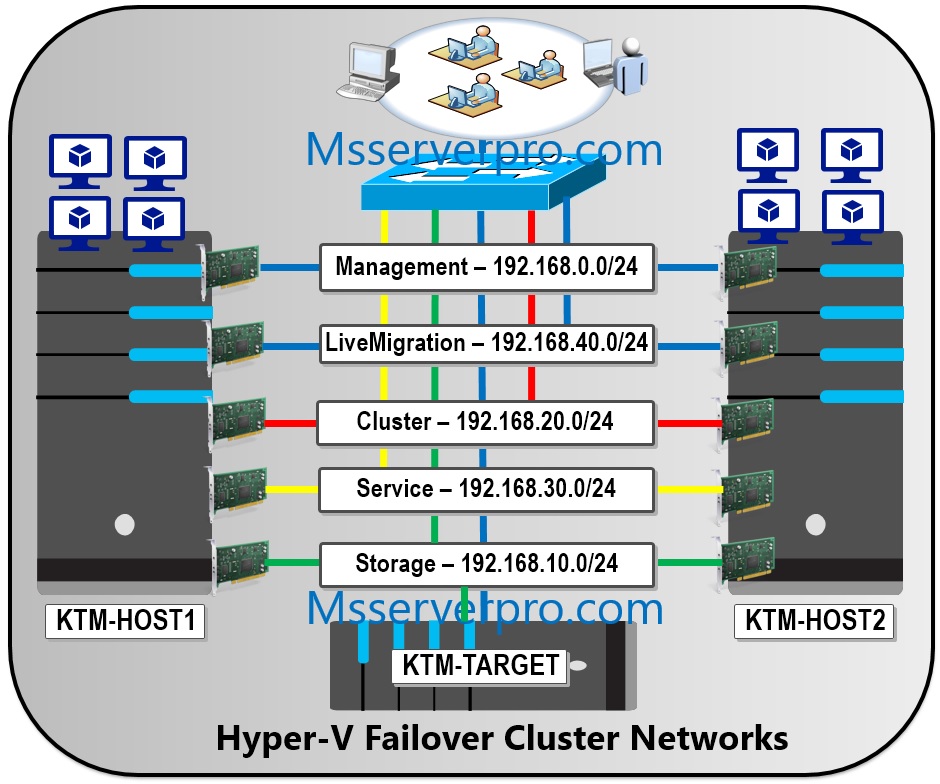
| Hyper-V Network Traffic Type | Description |
| Management Network | Provides connectivity between Hyper-V Hosts and Active Directory, DNS and management traffic to our Management OS.
Not recommended to use the same NIC for virtual machine access and cluster communication. Use VLAN for separate virtual machine traffic from the management network. |
| Cluster Network | Used for inter-node cluster communication such as the cluster heartbeat and Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) redirection. |
| Live migration | Used for virtual machines live migration between cluster nodes. |
| Storage Network | Used for SMB traffic or for iSCSI traffic, at least two network ports dedicated to the iSCSI network.
If you are not using iSCSI or SMB3 storage communication, storage network (NIC) is not required. FC-HBA used for Fibre Channel SAN technology and Direct Attached Storage (DAS) use the special connector for storage communication. |
| Service Network (Virtual machine access) | Used for virtual machine connectivity.
Typically requires external network connectivity to service client requests. Recommended to create a network team of NICs for higher network bandwidth. |
| Replica traffic | Used for virtual machine replication through the Hyper-V Replica feature. |
The following table shows the recommended settings for each type of network traffic:
| Network Type | Recommended Settings |
| Management Network | Both of the following:
Allow cluster network communication on this network Allow clients to connect through this network |
| Cluster Network | Allow cluster network communication on this network. Note: Clear the Allow clients to connect through this network check box. |
| Live Migration Network | Allow cluster network communication on this network. Note: Clear the Allow clients to connect through this network check box. |
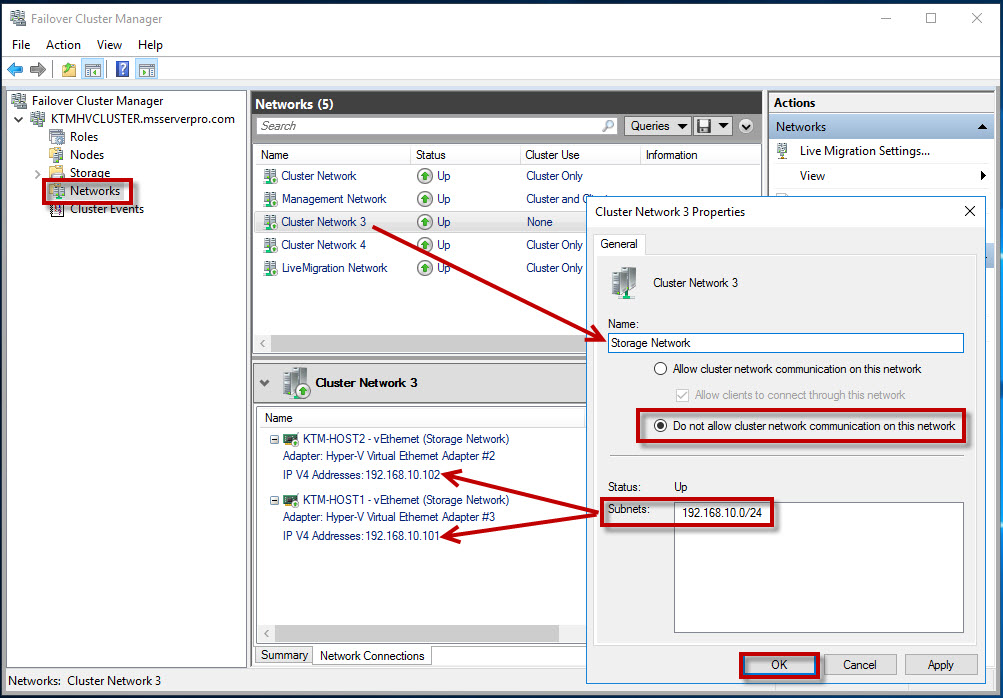
| Storage Network | Do not allow cluster network communication on this network |
| Service Network ( Virtual Machine) | Allow cluster network communication on this network |
| Replication Network
Note: Because of the hardware limitation in my lab, I have not included Replication Network. |
Both of the following:
Allow cluster network communication on this network Allow clients to connect through this network |
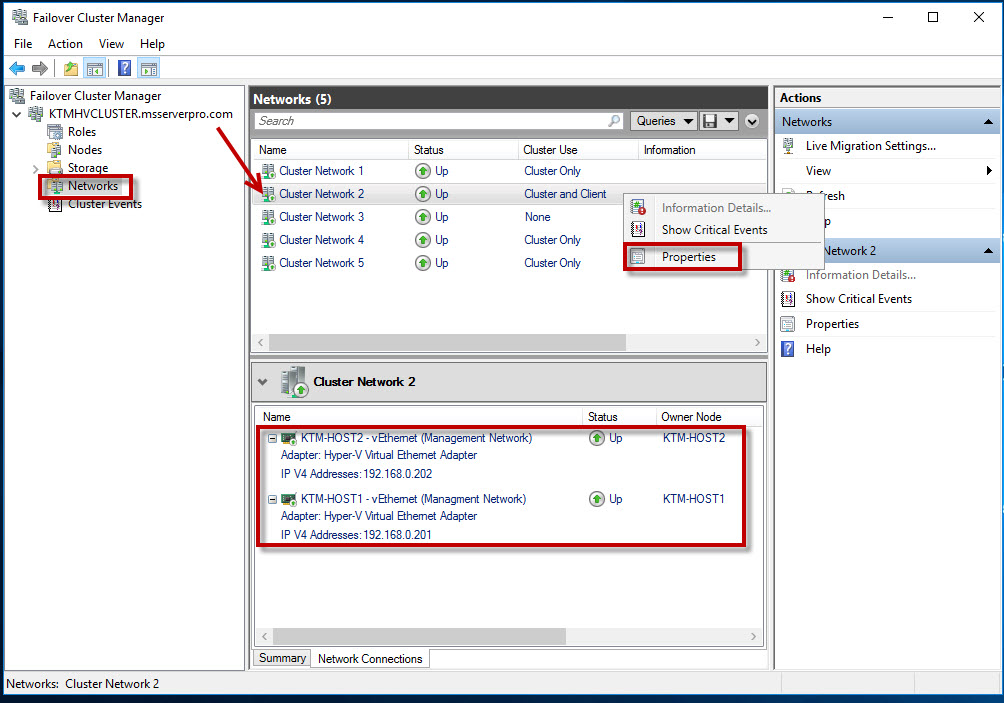
Management Network Settings:
- Allow cluster network communication on this network
- Allow clients to connect through this network

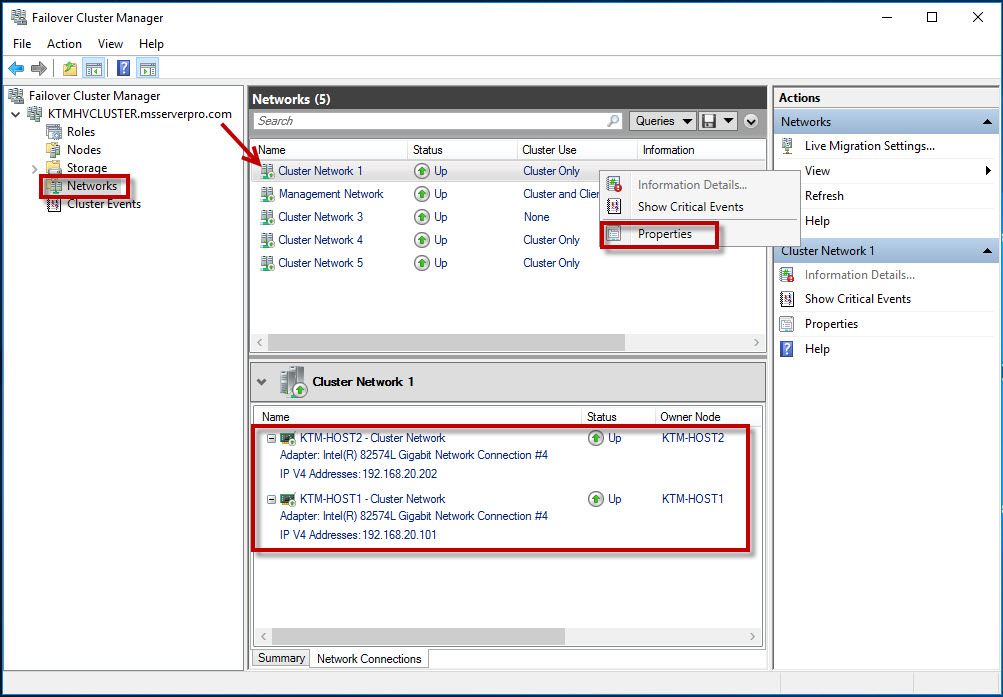
Cluster Network Settings:
- Allow cluster network communication on this network

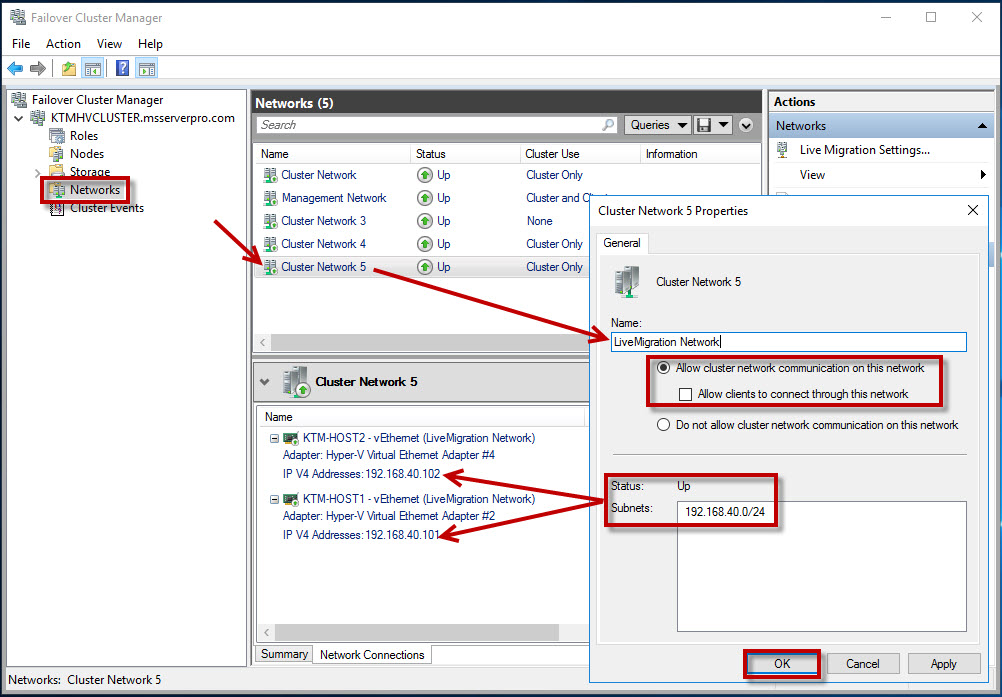
Live Migration Network Settings:
- Allow cluster network communication on this network
Storage Network Settings:
- Do not allow cluster network communication on this network
Service Network Settings:
- Allow cluster network communication on this network.

Isolate traffic on the live migration network:
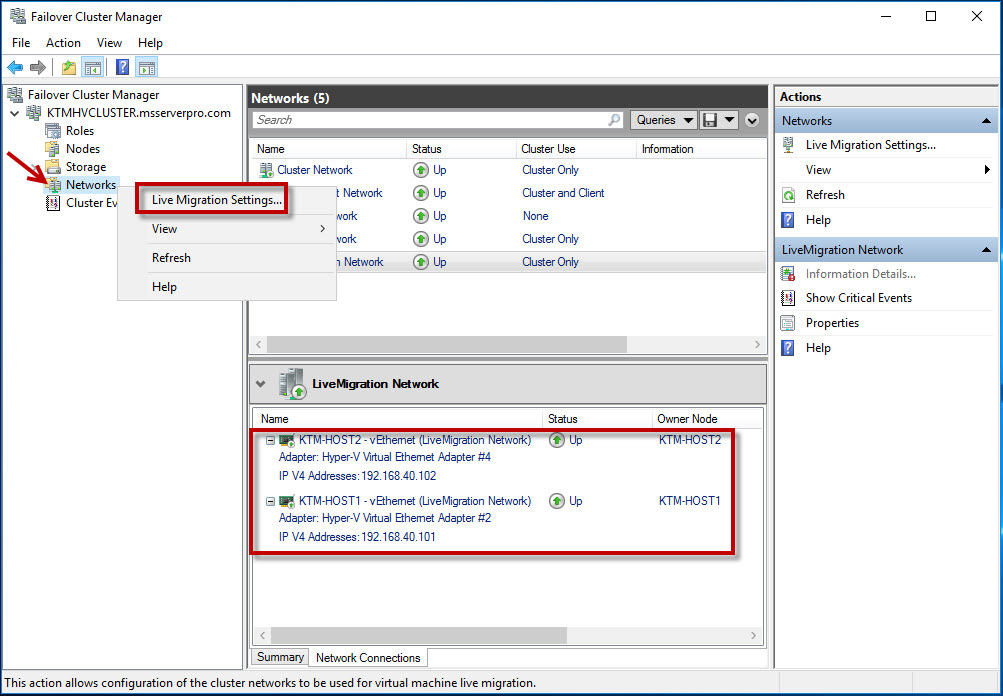
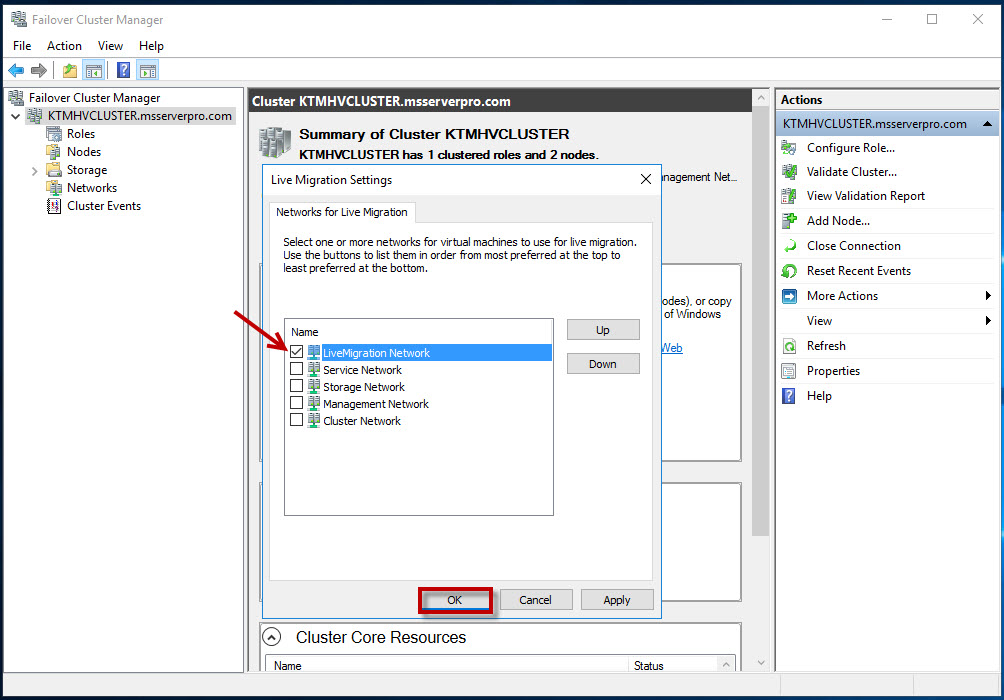
By default, live migration traffic uses the cluster network topology to discover available networks and to establish priority. However, you can manually configure live migration preferences to isolate live migration traffic to only the networks that you define. To do this, you can use Failover Cluster Manager or Windows PowerShell. To use Failover Cluster Manager, in the navigation tree, right-click Networks, and then click Live Migration Settings. Uncheck all the network except LiveMigration Network and click Up buttons to list LiveMigration Network in order from most preferred at the top.
Summary:
In the previous article, you had configure Implementing Failover Clustering with Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V. In this article, you have configure best practices on setting up Hyper-V Cluster Networks in Windows Server 2016 recommended network setting in Failover Cluster Manager. I hope this article helps network configuration setting for a Hyper-V failover Cluster in Windows Server 2016.









How can you verify that SMB traffic is flowing ONLY over the Storage network?
I don’t see that any isolation commands were ran, so wouldn’t it travel over any network possible?
answer is networking. just make sure that your smb or iSCSI originates from an ip that is in the same segment as the configured storage network. use vlan to let it reach the dedicated storage network nics of all nodes. this way it can only communicate in the storage network .
What about enabling network settings to enable both Cluster and Shared Nothing Live Migration?
Hi MS Server Pro,
Thank you for this post, but may i ask for your advice regarding Service Network (also used for VM network) and Management Network?
Say AD DNS is on the Management Network (say 192.168.0.X/24) while VM Network is on 192.168.30.X/24. How do you join the VMs to the domain while preventing them from talking to the Hyper-V hosts that are joined to the same domain?
Hi,
Can you please provide an indication for the bandwidth required for each type of network?
Thank you in advance
Service Network ( Virtual Machine) what is the purpose of this one? It is a vNic ( -managementOS), Virtual Machines will not see nor use it as it is and will be used by parent partition(host cluster nodes).
Great article!
Just on question about default gateways.
Out of all the networks a Hyper-V host has as recommended above, how many of the configured network adaptors have a default gateway set to reach external networks?
This is given that setting a second or further default gateway’s under Windows causes it to generate a Warning about redundancy and disjointed networks and hence will not always set one.
Excellent and thorough guide
Its terrible and incorrect.
First he says that Management network is just for host administration and that VM traffic will be on the Service Network.
Then in the actual configuration, he ALLOWS client traffic on the Management network and DISALLOWS client traffic on the Service network. If client is not checked, no VMs at all would be using Service
https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/askcore/2014/02/19/configuring-windows-failover-cluster-networks/
This is all based on 2008R2 NOT 2012 or 2016 and is NOT how Microsoft recommends configuring a Hyper-V Failover Converged Network.
We are looking at upgrading from 10Gb NICs to 40-100Gb NICs. But honestly I’m hoping I can get by with 2 physical NIC and use VLANs to separate traffic. We’d have redundancy in case we lose a NIC or upstream switch and I think that a single 40Gb or especially a 100Gb NIC would be more than enough bandwidth. I think I want to do the following but I am not sure if I can, or should
1) break up the 2 100Gb NICs into multiple Virtual NIC VLANs for different traffic VL10 VL20 VL30 VL40 VL50 VL60
2) Have a team that Hyper-v can use and allow VMs to use any VLAN via the Hyper-V VM setting
3) Use multiple non-teamed virtual NICs for iSCSI ( VL60-1 and VL60-2 ) for MPIO and redundancy
4) do I want to team other connections for migration/cluster/etc traffic or just use multiple IP addresses per cluster node ( easier )
Any advice would be appreciated
Hi all,
Thank you in advance. I am looking to setup a hyperv cluster. I need help in choosing a storage. I need to cluster 2 hosts and build 6 VM’s.
What storage can I use?